VOCs 废气治理的八大核心工艺解析
VOCs 废气作为工业生产与日常活动中常见的污染物,其治理需根据废气浓度、成分及排放要求选择适配工艺。以下八大核心处理工艺各有侧重,覆盖了从低浓度到高浓度、从简单成分到复杂混合物的治理需求。
VOCs waste gas, as a common pollutant in industrial production and daily activities, needs to be treated by selecting appropriate processes based on the concentration, composition, and emission requirements of the waste gas. The following eight core processing techniques each have their own focus, covering the treatment needs from low concentration to high concentration, from simple components to complex mixtures.
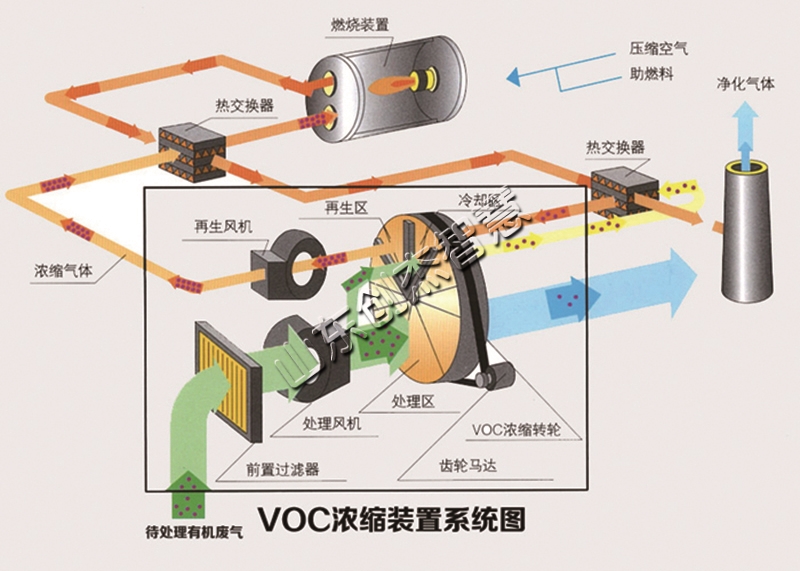
吸附法是应用最广泛的基础工艺,利用活性炭、分子筛等吸附剂的多孔结构,将 VOCs 分子截留于孔隙中。该工艺适用于低浓度、大风量废气,如印刷车间排放的溶剂蒸气,通过吸附剂吸附后可使废气达标排放。吸附剂饱和后需进行脱附再生(如热空气脱附、蒸汽脱附),再生后的 VOCs 可回收利用或焚烧处理,兼具环保与资源回收价值。
Adsorption method is the most widely used basic process, which utilizes the porous structure of adsorbents such as activated carbon and molecular sieves to trap VOCs molecules in the pores. This process is suitable for low concentration, high air volume exhaust gases, such as solvent vapors emitted from printing workshops. After adsorption by adsorbents, the exhaust gases can meet the emission standards. After the adsorbent is saturated, it needs to undergo desorption regeneration (such as hot air desorption, steam desorption). The regenerated VOCs can be recycled or incinerated, which has both environmental protection and resource recovery value.
催化燃烧法通过催化剂降低 VOCs 的燃烧温度,使有机物质在 200-400℃下氧化分解为 CO和 HO。相比直接燃烧,其能耗更低,适合中低浓度废气(浓度 1000-10000mg/m³),如涂装行业的喷漆废气。催化剂多采用贵金属(铂、钯)或非贵金属(铜、锰氧化物),需避免废气中的硫、氯等成分中毒失活,因此常配合预处理工艺去除杂质。
Catalytic combustion method reduces the combustion temperature of VOCs through catalysts, allowing organic matter to oxidize and decompose into CO and HO at 200-400 ℃. Compared to direct combustion, it has lower energy consumption and is suitable for low to medium concentration exhaust gases (concentrations of 1000-10000mg/m³), such as paint exhaust gases in the painting industry. Catalysts often use precious metals (platinum, palladium) or non precious metals (copper, manganese oxides) to avoid poisoning and deactivation of sulfur, chlorine, and other components in exhaust gas. Therefore, pre-treatment processes are often used to remove impurities.
蓄热式燃烧法(RTO) 依靠高温(800-1000℃)将 VOCs 彻底氧化,同时通过蓄热体回收燃烧热量,热效率可达 90% 以上。该工艺适用于高浓度废气(浓度>5000mg/m³),如化工反应釜排放的有机废气,即使废气成分复杂也能稳定处理。其核心是蜂窝状陶瓷蓄热体,通过交替切换气流方向实现热量循环,大幅降低运行能耗。
The regenerative combustion method (RTO) relies on high temperature (800-1000 ℃) to thoroughly oxidize VOCs, while recovering combustion heat through a thermal storage body, with a thermal efficiency of over 90%. This process is suitable for high concentration waste gas (concentration>5000mg/m³), such as organic waste gas emitted from chemical reaction vessels, and can be stably treated even if the composition of the waste gas is complex. Its core is a honeycomb shaped ceramic thermal storage body, which achieves heat circulation by alternately switching the airflow direction, significantly reducing operating energy consumption.
吸收法利用 VOCs 在吸收剂中的溶解度差异实现分离,分为物理吸收(如柴油吸收苯系物)和化学吸收(如碱液吸收有机酸)。该工艺适合处理水溶性或易反应的 VOCs,如制药行业的含醇废气,吸收后的富液可通过蒸馏解析回收溶剂,吸收剂循环使用。需注意吸收剂的选择,避免二次污染且确保吸收效率稳定。
The absorption method utilizes the difference in solubility of VOCs in absorbents to achieve separation, which is divided into physical absorption (such as diesel absorption of benzene derivatives) and chemical absorption (such as alkaline absorption of organic acids). This process is suitable for treating water-soluble or easily reactive VOCs, such as alcohol containing waste gas in the pharmaceutical industry. The absorbed rich solution can be recovered by distillation and solvent recovery, and the absorbent can be recycled. Attention should be paid to the selection of absorbents to avoid secondary pollution and ensure stable absorption efficiency.

冷凝法通过降温使 VOCs 从气态冷凝为液态,适合高浓度、高沸点 VOCs(如油气回收中的汽油蒸气),常作为预处理工艺与其他方法联用。冷凝温度越低,回收效率越高,可配合冷冻机组将温度降至 - 30℃至 - 100℃。回收的液态 VOCs 可直接回用,适合溶剂型企业实现资源循环,但对低沸点物质处理效率有限。
The condensation method condenses VOCs from a gaseous state to a liquid state through cooling, which is suitable for high concentration, high boiling point VOCs (such as gasoline vapor in oil and gas recovery), and is often used in combination with other methods as a pretreatment process. The lower the condensation temperature, the higher the recovery efficiency. It can be combined with a refrigeration unit to lower the temperature to -30 ℃ to -100 ℃. The recycled liquid VOCs can be directly reused, which is suitable for solvent based enterprises to achieve resource recycling, but the efficiency of treating low boiling point substances is limited.
生物处理法利用微生物代谢作用分解 VOCs,将其转化为无害的生物质和 CO。该工艺包括生物滤池、生物滴滤等形式,适合低浓度(<1000mg/m³)、易生物降解的 VOCs,如食品加工行业的发酵废气。优势是运行成本低、无二次污染,但受温度、湿度影响较大,对难降解物质(如苯、甲苯)处理效率较低。
The biological treatment method utilizes microbial metabolism to decompose VOCs and convert them into harmless biomass and CO. This process includes forms such as biofilters and biofilters, and is suitable for low concentration (<1000mg/m³) and easily biodegradable VOCs, such as fermentation waste gas in the food processing industry. The advantages are low operating costs and no secondary pollution, but it is greatly affected by temperature and humidity, resulting in lower efficiency in treating difficult to degrade substances such as benzene and toluene.
等离子体法通过高压电场产生高能电子,破坏 VOCs 分子结构使其分解。适用于低浓度、多组分废气,如电子行业的光刻废气,处理过程快速且设备占地面积小。但需注意避免产生 NOx 等二次污染物,且对高浓度废气处理能耗较高,通常作为辅助工艺使用。
The plasma method generates high-energy electrons through a high-voltage electric field, which breaks down the molecular structure of VOCs and decomposes them. Suitable for low concentration, multi-component exhaust gases, such as lithography exhaust gases in the electronics industry, with fast processing and small equipment footprint. However, attention should be paid to avoiding the generation of secondary pollutants such as NOx, and high energy consumption is required for the treatment of high concentration exhaust gas, which is usually used as an auxiliary process.
光催化氧化法借助紫外线激发 TiO等光催化剂,产生羟基自由基氧化分解 VOCs。适合低浓度、恶臭类废气(如污水处理厂的臭气),设备简单易维护,但受光照强度、催化剂活性影响,处理效率易波动,需定期更换催化剂以保证效果。
The photocatalytic oxidation method utilizes ultraviolet light to excite photocatalysts such as TiO, generating hydroxyl radicals to oxidize and decompose VOCs. Suitable for low concentration and odorous exhaust gases (such as the odor from sewage treatment plants), the equipment is simple and easy to maintain, but the treatment efficiency is easily affected by light intensity and catalyst activity, and the catalyst needs to be replaced regularly to ensure effectiveness.
VOCs 废气治理需遵循 “分质施策” 原则,八大工艺各有适用场景:高浓度废气优先选择蓄热燃烧或冷凝回收,中低浓度废气可采用催化燃烧或吸附法,复杂成分废气常采用 “预处理 + 主工艺” 的组合方案。合理选择工艺不仅能实现达标排放,更能兼顾能耗与资源回收,推动废气治理从 “末端控制” 向 “综合利用” 升级。
The treatment of VOCs waste gas should follow the principle of "targeted treatment based on quality", and each of the eight processes has its own applicable scenarios: high concentration waste gas should be prioritized for thermal storage combustion or condensation recovery, medium and low concentration waste gas can be treated using catalytic combustion or adsorption methods, and complex component waste gas often adopts a combination of "pretreatment+main process". Reasonable selection of processes can not only achieve standard emissions, but also balance energy consumption and resource recovery, promoting the upgrading of waste gas treatment from "end of pipe control" to "comprehensive utilization".
本文由VOCs废气处理友情奉献.更多有关的知识请点击:http://www.sdcjtz.com我们将会对您提出的疑问进行详细的解答,欢迎您登录网站留言.
This article is dedicated to the automatic shot blasting machine and friendship For more information, please click: http://www.sdcjtz.com We will provide detailed answers to your questions. You are welcome to log in to our website and leave a message
上一篇:揭秘机器人涂装线:工业美学背后的 “机械交响乐团”
下一篇:















 鲁公网安备 37142502000144号
鲁公网安备 37142502000144号